Abstract
The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the effects of Nitric Oxide Dump (NOD) exercise on Blood Pressure (BP) levels of hypertension patients. For this purpose, twenty (20) moderate hypertension patients of Takhte Nasrate, Karak District were selected as subjects at random. A randomized pretest-posttest Equivalent-Group Design was used in the current study. As a result, ten (10) subjects were included in the Experimental Group (EG) and the same number of subjects i.e. ten (10) were included in the Control Group (CG). The EG was given a 6-week NOD exercise for low intensity for 3 weeks, medium intensity for 3 weeks and high intensity for 1 week. Results indicated that NOD exercise helped in reducing the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients. The results obtained through the current study justify the use of nitric dump oxide exercise, as one of the important interventions to reduce blood pressure levels of hypertension patients.
Key Words
Effects, Nitric Dump Exercise, Blood Pressure, Middle-aged & Hypertension Patients
Introduction
Though a lot of adults have the disorder of hypertension, figural it is surmised that almost 25% of world adults have hypertension disease or have some traces of hypertension. Besides that, looking at the speed and effect of hypertension it is estimated that it may have a surge of 60% by 2025, so it becomes an international problem, that how we can dominate and control hypertension (Kearney, Whelton, Reynolds, Muntner & Whelton, 2005). Previous various schooling regarding hypertension has cleared that risk factors (e.g., age, BMI, physical inactivity) have a gigantic effect on stroke and heart diseases (Mancia, et al., 2007). The World Health Organization (WHO, 2021), interpreted that almost one billion (1.13 bn) human beings are diagnosed with hypertension. As it has no proper symptoms it acted as a silent killer in the 21st century and is a vital issue concerning public health across the world. Hypertension causes many big uncurable heart issues such as stroke, cardiac diseases, kidney failure, blindness, including early age demise.
Different countries have different estimations in respect of hypertension. A developing country like the United States (US) has almost 680 lac cases of hypertension registered. Among them, 480 lac people were nursing pharmacologically and almost 310 Lac had managed their situation Prevention (US). Office of Public Health Preparedness. (2011). Likewise, a 2013 survey by the American Heart Association shows that the main reason for the demise of 348,102 human beings is High Blood Pressure (HBP). Similarly, Hypertension is common (almost 31% of people have hypertension) in New Zealand almost every third has this disorder (McLean, Williams, Mann, Miller & Parnell, 2013). Because hypertension is linked to a variety of cardiovascular ailments, it is considered one of the most pressing public health issues in the United States (Fryar, Ostchega, Hales, Zhang & Kruszon, 2017). In the USA every second person has hypertension and 39.64% have regulated their hypertension properly with medicines (Chobufo et al., 2018). In 2017 public health survey in England surmised that 118 lac adults aged more than 15 had hypertension, this is 26.2% of their adult population, so almost every fourth adult has hypertension. Likewise, in 2017 almost 41 lacs are surmised to have hypertension of which 21.6% are properly controlled with medication and 17% medicated but were not in control (Hird et al., 2019). Four hundred thirty (430) lack of Japan's population had hypertension and only half of them were treated, almost 1/4th were controlled (Hirawa and Umemura, 2019). Over 50% of people in China live in a rural areas so there is a probability that they will be ignorant of hypertension and its control, that’s why it is not treated well and is not controlled in spite of high knowledge (Xing et al., 2020).
As for the estimation of hypertension in under-developing countries is concerned, it is reported that the risk of death from hypertension has increased by 25% in less than a decade in South Africa (Ibrahim and Damasceno, 2012). Likewise, this surge in hypertension has a high impact on health causing different health issues as hypertension is the major reason for adult death in improving countries (Olives, Myerson, Mokdad, Murray & Lim, 2013). Similarly, in cities, India has 33 per cent and in the village area, they have 25 per cent of hypertension patients and only 25 per cent of village people and 42 per cent of city people know about their hypertension level. 25 per cent of village people and 38 per cent of city people are medicated for hypertension in India (Anchala et al., 2014). The customariness of HP in Indonesia is very fast and schooling to its slow and low, medication is very slow and low level and a lot of medical training and surveys are required on urgent bases to improve awareness and medication of hypertension (Peltzer and Pengpid, 2018). In Indonesia, hypertension spreads very fast among youngsters and it may affect their (youngster) natural level habits and etiquette, now to alter the spreading level of hypertension in grown-up life habits and behaviour of them should be the first thing to consider (Kurnianto et al., 2020). Here in Pakistan, 18 per cent of the mature have hypertension and of people aged more than 45 are 33 per cent, who face the issue of hypertension. And only half of these patients are medicated and among these only 12 per cent were properly managed (Zafar et al., 2018).
There are different causes of hypertension. according to one study, the cause of hypertension includes obesity, high alcohol consumption, rich salty material eating ageing and may be sedentary lifestyle a lot of pressure and depression potassium intaking or taking less amount of calcium (Carretero and Oparil, 2000). The initial one is the basic necessary of hypertension which has not any proper clear reason or causes but it seems that it results in proper compound matrilines or hereditary issues and natural surrounding agents and the following hypertension is caused by the proper basic process of kidneys or endocrine system of the human being (Pedrosa et al., 2011). Another casual reason for hypertension is chronic kidney disease in this disease kidney does not remain able to separate liquids inside it and its quantity increases and resulting in hypertension (de Pinho et al., 2019). As per the world health organization (2021) survey the key causes of hypertension are lack of no proper diet, avoiding physical venture, and intake of alcohol in rich quantities and tobacco. Worldwide 71 lac human beings died because of hypertension (high blood pressure).
Different strategies are developing to control hypertension and physical activity is considered one of the important tools in this regard. Therefore, the findings of the studies reveal that physical activity can help in preventing the health problem of hypertension (Whelton et al., 2002; Hasnain, 2007). These insights were gleaned from related literature demonstrating the beneficial effects of physical activity and exercise on health. In this regard, a previous study to determine the effects of exercise on avoiding high blood pressure was conducted (Paffenbarger, Thorne & Wing, 1968). Taking this into account, Boyer and Kasch (1970) conducted an interventional study to investigate the effect of exercise on blood pressure (BP) and found that an aerobic interval training programme of two (02) days per week reduced BP in various circumstances.
From previous study and research, it is clear that physical activities and exercise are good for many cardiovascular diseases as it helps in decreasing the chances of being diagnosed with these diseases and it is very easy pre-health safety having very less bad effects but if it is done properly with World Health Organization (WHO) suggested instruction, and rules and everyone has proper physique including muscles, blood, bones and many other different alive tissues (Moreau et al., 2001). Proper routine physical activities will surge galloping level and speed, avert ageing, and nourish muscle and the cardiovascular system. It will also increase your sporting expertise and skills (Penedo and Dahn, 2005). Studying archived accident, cases and causes of hypertension shows that exercise and the physical venture has a positive impact on human being decreasing a person's blood pressure and combining results of different scientific studies addressing hypertension and its causes, shows that aerobic exercise decreases blood pressure level (Choudhury et al., 2005). Jogging is the easiest and pretty much safe type of training for every genre of hypertension patient. So past studies show that walking, and cycling have a fruitful effect in controlling hypertension (Collier et al., 2008). Further studies declare that a lot of hypertension-diagnosed persons have very high weight so walking exercises will not be easy for them to do. And doing routine proper physical activities will power up the immune system and will aid in the fight against cardiovascular diseases (Abou-Elmagd, 2016). Regular exercise plays a vital role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, helps in reducing blood pressure, and can help with blood lipid abnormalities, diabetes and obesity (Gulam, 2016).
There is a new version of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) that is called a Nitric Oxide Dump (NOD) exercise which helps in discharging nitric oxide, which ultimately helps in catalysis and will remove ill health. Nitic oxide occurs in the very internal layer of the blood vessel (endothelium) of a human being. It has a molecule for carrying molecule which carries signals to different cells in different parts of the body, for example, the nervous system, backbone etc. and as it is discharged by doing train, nitric oxide performs in the soft muscles and keeps them calm. Nitric oxide dump has a very plain mobility doing it very fast in a small time which will give advantages like long time exercise, but as I said that it will happen in small time instead of a long time. Bush (scientist) name it the most beneficial and finish type of exercise to boost up your body. As it takes very time of 180 to 240 sec and you have to do it 3 times a day so it will take very less time almost 15 minutes.
Over the previous four to five decades, a large body of literature has typically produced consistent conclusions about the defensive effects of exercise in the prevention of hypertension. However; different unanswered questions remain under debate in respect of the optimum treatment for the control and prevention of hypertension (Diaz & Shimbo, 2013). Therefore, several recent studies both prospective (Hu et al., 2004) and meta-analysis (Wen & Wang, 2017) conducted to determine the role of physical activities in the prevention of hypertension and may help to direct some of the early unanswered questions. However, an interventional study in this area especially in the territory of Pakistan regarding the effects of nitric oxide dump exercise in the prevention of hypertension has not so far been conducted yet. Therefore, the current study was conducted to determine the effects of Nitric Oxide Dump exercise (NOD) on blood pressure levels of middle age hypertension patients.
Hypertension appears to worsen a variety of illnesses as well as the risk of complications such as heart attack or stroke, impaired kidney function, and the need for dialysis. As a result, research in the fields of exercise and hypertension control is becoming increasingly relevant among scientists. Previous studies focused on prospective (Hu et al., 2004), epidemiological (Choudhury et al., 2005) and meta-analysis (Wen & Wang, 2017), but there has no research study so far been conducted determining the effects of Nitric Oxide Dump exercise (NOD) upon blood pressure levels of middle age hypertension patients. To get an objective measurement regarding the effect of NOD exercise, an interventional study is required. Focusing on hypertension patients can help develop and suggest exercise protocols of preventive measures for this increasing health issue. Additionally, it will provide information for health and other related think tanks to devise policies to implement NOD exercise. Therefore, the reason for the current research work was to assess the effects of NOD exercise on blood pressure levels (BPL) of middle-aged hypertension patients. A quasi-experimental study was conducted to get an objective measurement of the supervised exercise among hypertension patients in the territory of District Karak, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP), Pakistan.
Objectives
The study's objectives were as follows:
1. To assess the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients of the control group and experimental group pre-test.
2. To assess the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients of the control group and experimental group pos-test.
3. To compare the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients of the control group in pre-test and post-test.
4. To compare the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients of the experimental group in pre-test and post-test.
Research Hypothesis
The researcher has focused to obtain the following hypothesis
H0: There is no significant difference between the blood pressure levels of the control group and the experimental group in the pre-test.
H0: There is no significant difference between the blood pressure levels of the control group and the experimental group post-test.
H0: There is no significant difference in blood pressure levels of the control group between the pre-test and post-test.
H0: There is no significant difference in blood pressure levels of the experimental group between the pre-test and post-test.
Methods and Materials
The methodology is a complete process applied to
research work. It includes various steps and methods to be taken by a researcher in order to reach certain findings and conclusions. Therefore, this chapter of the current study describes the detailed procedures adopted for the selection of subjects, research design, randomization, research variables, training program administration and statistical analysis.
Selection of Subjects
A proper screening method was used for the confirmation of the diagnosis of hypertension based on Systolic Blood Pressure=121-139 mm Hg and Diastolic Blood Pressure=81-89 mm Hg. In addition, subjects were asked about their personal and family history of blood pressure, risk factors associated with medication and treatment, eating habits and diet, and current daily physical activity habit.
Research Design
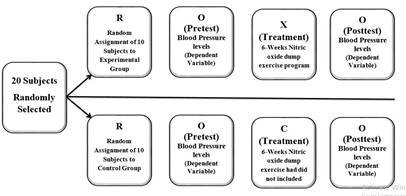
A randomized pretest-post-test Equivalent-Group Design was used in the current study. Pre-tests are given before the experimental and control treatments are applied, and post-tests are given at the end of the treatment period in this sort of study. The pre-test score can be used in covariance analysis to statistically adjust for any differences between groups at the start of the investigation. An example of pretest-post-test Equivalent Group Design is given in the following figure:
Figure 1
More significantly, a Pre-test was conducted to check whether or not the Two Groups are Really similar.
Randomization
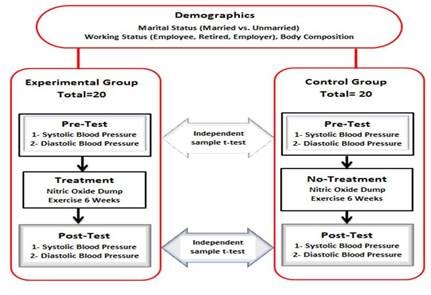
The researcher used online tables of random numbers for the allocation of subjects. Two groups of subjects were used, with both groups being measured or observed twice. The first group was called an Experimental Group (EG), to which the experimental treatment (6-week nitric oxide dump exercise) was given. EG was denoted by 'X'. The second group was named as Control Group (CG), to which the treatment was not given. CG was denoted by 'C'. Random assignment was used from the groups. As a result, ten (10) subjects were included in EG and the same number of subjects i.e., (10) were included in CG. The first measurement acted as a pre-test, while the second served as a follow-up. Both groups had their measures taken at the same time. A diagram is given for better understanding.
Figure 2
Research Variables
In this research study, the following independent and dependent variables were studied.
Independent Variables
Nitric Oxide Dump (NOD) exercise was taken as an independent variable. A detailed description of NOD is given as under;
Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise
Nitric Oxide Dump exercise (NODE) is that exercise which is designed to increase the nitric oxide (NO) in the body and maintain overall health. The NODE takes a short period of time, this exercise consists of one session and the duration of this season are three to four minutes repeat this exercise two times a day. The nitric oxide dump exercise (NODE) consisted of;
The Squat
A squat is an exercise in which the body lowers its hips from a static position and then stands back up this exercise is the best and easy for reducing blood pressure levels and also maintaining the all-body muscles.
Circular Arm Swing
Stand with a static position and extent your arm parallel and circle your arms forward using controlled motions, gradually making the circles.
Shoulder Press
Expand the arms till they reach overhead and back
the motion to go back the bar to the chest and deltoids, upper chest, shoulder and elbows pointing forwards.
Static Forward March
With your feet together and arms at your sides, stand tall. As you lift your legs, bend your elbows and swing your arms. There are a variety of March styles to choose from, including as
? March is in place.
? March four steps forward.
? Four steps back.
Dependent Variables
Blood pressure levels were considered as a dependent variable.
Blood Pressure Levels
According to the world health organization (2021), blood pressure is defined as “Blood pressure (BP) is the force or pressure of blood pushing against blood walls”. Blood pressure can be represented in numbers. One is systolic blood pressure and the other is diastolic blood pressure.
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)
Systolic blood pressure is defined as the pressure in blood vessel walls when the heart contracts. It means that the contraction of the heart is called systolic blood pressure. Systolic blood pressure was measured with the help Blood Pressure Monitor.
Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP)
Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) means the contraction of the heart. A diagram has been given to show the variables model used in the current study. Likewise, Diastolic pressure was measured with the help Blood Pressure Monitor.
Training Program
The EG was given a 6-week NOD exercise with low intensity for 3 weeks, medium intensity for 3 weeks and high intensity for 1 week. The training was given five days per week. Every session lasted for 14 minutes. It's worth noting that the training was set for the morning, from 8 a.m. to 8.30 a.m.
Prior to and during each session, the subjects were closely monitored as they went through their assigned programme. Warm-up and cool-down exercises comprised running, stretching, striding, and push-ups for a total of 05 minutes.
For the training groups, attendance was calculated by dividing the total members of training sessions by the number of sessions provided. The overall attendance report was rated as satisfactory, with a score of 90%.
Administration and Organization of the Training Program
The researcher conducted the NOD exercise program at the Local Ground, Village Bogara, District Karak. The researcher personally supervised and ensured the proper execution of the NOD training with the help of a local coach.
Six (6) weeks of exercise protocols comprised of nitric oxide dump exercises were developed and employed on hypertension patients
Table 1.
|
Two Time Per Day M/E |
Nitric Oxide Dump
Exercise Protocol |
|||||||||
|
The Squat |
Circular Arm Swing |
Shoulder Press |
Static
Forward March |
Time Interval |
||||||
|
Rep |
Set |
Rep |
Set |
Rep |
Set |
Rep |
Set |
|
||
|
Week 1 |
7 |
5 |
7 |
5 |
7 |
5 |
7 |
5 |
150 sec |
|
|
Week 2 |
8 |
5 |
8 |
5 |
8 |
5 |
8 |
5 |
150 sec |
|
|
Week 3 |
9 |
4 |
9 |
4 |
9 |
4 |
9 |
4 |
120 sec |
|
|
Week 4 |
10 |
4 |
10 |
4 |
10 |
4 |
10 |
4 |
90 sec |
|
|
Week 5 |
11 |
3 |
11 |
3 |
11 |
3 |
11 |
3 |
90 sec |
|
|
Week 6 |
12 |
3 |
12 |
3 |
12 |
3 |
12 |
3 |
60 sec |
|
Results and Discussion
Table 2. Frequencies
and Percentages of the Sample in Respect of their Demographic differences.
|
Demographic |
Categories |
Frequency |
Per cent |
|
Group |
Experimental |
10 |
50.0 |
|
Control |
10 |
50.0 |
|
|
Total |
20 |
100.0 |
|
|
Marital Status |
Married |
15 |
75.0 |
|
Unmarried |
5 |
25.0 |
|
|
Total |
20 |
100.0 |
|
|
Working Status |
Employee |
13 |
65.0 |
|
Retired |
7 |
35.0 |
|
|
Total |
20 |
100.0 |
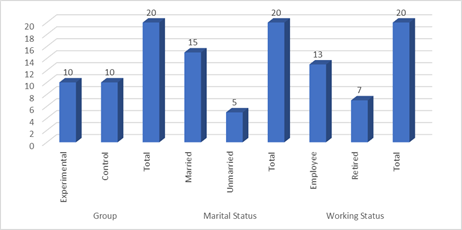
Figure 5
Frequency of Respondents in Respect of their Demographic Attributes
Table 4.1 and figure 4.1 are showing the frequency and
percentage of the demographic variables of the participants. In Table 4.1 two
groups (experimental & control) are mentioned. Ten (10) subjects were
included in an Experimental Group and the same number of subjects were included
in the Control Group. The second demographic variable was marital status. The
frequency of the married was 15 and unmarried was 5. The nest demographic
variable was working status. The frequency of the respondents was 20 of which
employees were 13 and retried were 7.
Table 3. Descriptive Anthropometric
Measures of the Sample
|
Anthropometric |
N |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Mean |
Std. Deviation |
|
Height |
20 |
168.00 |
177.00 |
173.5500 |
2.62528 |
|
Weight |
20 |
70.00 |
77.00 |
73.2500 |
2.22131 |
|
Body Mass Index |
20 |
22.66 |
26.57 |
24.3360 |
1.08830 |
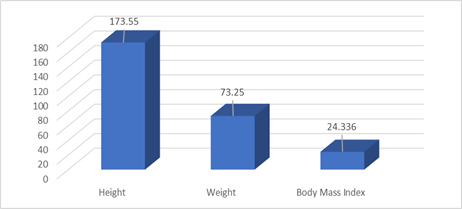
Figure 4
Bar Graph of Anthropometric Measures of the Respondents
Table 4.2 and figure 4.2
shows the details of the astrometric measurements of the participants. In this
regard, Height, weight and body Mass Index were measured and their measurements
are presented in the above table. According to the table, the age-wise mean was
47.7, the standard deviation was 6.25, and the height-wise mean was 173. 55,
the standard deviation was 2.62, the weight-wise mean was 73.25, and the
standard deviation was 2.22. The mean of the body mass index was 24.33 and the
standard deviation was 1.08.
Testing of
Hypotheses
Table 4. Independent Sample
t-test Showing the mean difference between the Blood Pressure Levels of the Experimental
Group and Control Group before the Treatment.
|
Testing Variables |
Group |
N |
Mean |
Std. Devi: |
t |
Sig. |
|
Pre-test Diastolic |
Experimental |
10 |
84.2000 |
2.61619 |
.453 |
.656 |
|
Control |
10 |
83.7000 |
2.31181 |
|
|
|
|
Pre-Test Systolic |
Experimental |
10 |
135.4000 |
2.63312 |
.856 |
.403 |
|
Control |
10 |
134.4000 |
2.59058 |
|
|
Table 4.3 shows the mean difference between the intervention
group and control group in respect of their
Diastolic and Systolic blood pressure levels before the treatment. The
mean Diastolic blood pressure level of the intervention group was 84.20±2.61
and control group was 83.70±2.31, according to the t-statistics the mean
difference was insignificant (t= .453, sig.= .656 > ?= 0.05) because the
sig. value of Table 4.3 was greater than the alpha level of 0.05.
In the same way, the mean
systolic blood pressure level of the intervention group was 135.40±2.63 and
control group was 134.40±2.59, according to the t-statistics the mean
difference was insignificant (t= .453, sig.= .656 > ?= 0.05) because the
sig. value of Table 4.3 was greater than the alpha level of 0.05.
Hence, the researcher concluded that there is no significant
difference between blood pressure levels (Diastolic and Systolic) of the
control group and the experimental group in the pretest.
HI: There is a
significant difference between the blood pressure levels of the control group and
the experimental group in post-test.
Table 5. Independent Sample
t-test showing the mean difference between the Blood Pressure Levels of the Experimental
Group and Control Group after the Treatment.
|
Tests |
Group |
N |
Mean |
Std. Devi: |
T |
Sig. |
|
Post-test Diastolic |
Experimental |
10 |
80.9000 |
1.28668 |
-3.050 |
.007 |
|
Control |
10 |
83.5000 |
2.36878 |
|
|
|
|
Post-test Systolic |
Experimental |
10 |
118.9000 |
31.95292 |
-1.439 |
.043 |
|
Control |
10 |
133.5000 |
2.99073 |
|
|
Table 4.4 shows the mean difference between the intervention
group and control group in respect of their Diastolic and Systolic blood
pressure levels after the treatment. The mean Diastolic blood pressure level of
the intervention group was 80.90±1.28 and the control group was 83.50±2.36.
According to the t-statistics, the mean difference was significant (t= -3.050,
sig.= .007 < ?= 0.05), because the sig. value of Table 4.4 for diastolic was
less than alpha level 0.05. The mean of the intervention group was less than
the control group in diastolic blood pressure (80.90 < 83.50) which
indicates that the diastolic blood pressure level of the experimental group was
better than the control group the mean difference was recorded as 2.6 mmHg.
The
mean Systolic blood pressure level of the intervention group was 118.90± 31.95 and control group was 133.50±2.99,
according to the t-statistics the mean difference was significant (t=
-1.439, sig.= .043 < ?= 0.05) because the sig. value of Table 4.4 for
systolic was less than alpha level 0.05. The mean of the intervention group was
less than the control group in Systolic blood pressure (118.90 < 133.50)
which indicates that the systolic blood pressure level of the experimental
group was better than the control group the mean difference was recorded as 15
mmHg.
The data shows that the
nitric oxide dump exercise produced a positive effect on the blood pressure level of the experimental
group. Hence, the researcher concluded that there is a significant difference between the blood
pressure levels of the control group and the experimental group (nitric
oxide dump exercise) in the post-test.
H0: There is no significant difference in blood
pressure levels (Diastolic and Systolic) of the control group between the
pre-test and post-test.
Table 6. Paired Sample t-test
showing the mean difference between the Blood Pressure Levels of the Control
Group before and after the Treatment.
|
Pair
|
Tests |
Mean |
N |
Std. Devi: |
r |
T |
Sig. |
|
Pair 1 |
Pre-test Diastolic |
83.7000 |
10 |
2.31181 |
.801 |
.429 |
.678 |
|
Post-test Diastolic |
83.5000 |
10 |
2.36878 |
|
|
|
|
|
Pair 2 |
Pre-Test Systolic |
134.4000 |
10 |
2.59058 |
.860 |
1.868 |
.065 |
|
Post-test Systolic |
133.5000 |
10 |
2.99073 |
|
|
|
Table 4.5 shows the results of paired sample t-test regarding
the pre-test and post-test results of the diastolic and systolic blood pressure
levels of the control group. The mean score of diastolic blood pressure level
in the pre-test was 83.70±2.31 and in the post-test was 83.50±2.36.
According to the
t-statistics, this mean difference was insignificant in diastolic blood
pressure level (t=.429, Sig.= .678 > ?= 0.05) because the sig. value of the
data was greater than the alpha level of 0.05. The results of r also support
the results of t because the pre-diastolic and post-diastolic were 80%
correlated as well as pre-systolic and post-systolic were 86% correlated in the
control group.
In the same way, the mean score of systolic blood pressure
level in the pre-test was 134.40±2.59 and in the post-test was 133.50±2.99.
According to the t-statistics, this mean difference was insignificant in
systolic blood pressure level (t= 1.868, Sig.= .065 > ?= 0.05) because the
sig. value of the data was greater than the alpha level of 0.05.
The results of the
diastolic and systolic blood pressure levels of the control group in pre- and
post-test indicate that the control group remained the same in both tests and
no significant change in blood pressure level occurred without any treatment.
Hence,
the hypothesis that there is no significant
difference in blood pressure levels (Diastolic
and Systolic) of the control group between the pre-test and post-test is
accepted.
H0: There is no Significant difference in Blood
Pressure Levels of the Experimental Group between the Pre-test and Post-test.
Table 7. Paired Sample t-test
showing the mean difference between the Blood Pressure Levels of the Experimental
Group before and after the Treatment.
|
Pair |
Tests |
Mean |
N |
Std. Devi: |
r |
T |
Sig. |
|
Pair 1 |
Pre-test Diastolic |
84.2000 |
10 |
2.61619 |
.733 |
5.521 |
.000 |
|
Post-test Diastolic |
80.9000 |
10 |
1.28668 |
|
|
|
|
|
Pair 2 |
Pre-Test Systolic |
135.4000 |
10 |
2.63312 |
.655 |
1.634 |
.043 |
|
Post-test Systolic |
118.9000 |
10 |
31.95292 |
|
|
|
Table 4.6 shows the important results of paired sample t-test
regarding the pre-test and post-test results of the diastolic and systolic
blood pressure levels of the invention group. The mean score of diastolic blood
pressure level in the pre-test was 84.20±2.61 and in the post-test was
80.90±1.28. According to the t-statistics, this mean difference was significant
in diastolic blood pressure level (t=.5.521, Sig.= .000 < ?= 0.05), because
the sig. value of the data was less than the alpha level of 0.05.
In the same way, the mean score of systolic blood pressure
level in the pre-test was 135.40±2.63 and in the post-test was 118.90±31.95,
according to the t-statistics this mean difference was significant in systolic
blood pressure level (t= 1.634, Sig.= .043 < ?= 0.05) because the sig. value
of the data was less than the alpha level of 0.05.
Discussion
The main purpose of the study was to assess the effects of nitric oxide dump exercise on blood pressure levels of middle age hypertension patients. The independent variable of the study was nitric oxide dump exercise and the dependent variable was blood pressure. Twenty (20) patients with middle-aged hypertension determinants were selected after studying the literature in depth and counselling the researcher supervisor.
After the data analysis, the researcher found that there is a significant effect of nitric oxide dump exercise on blood pressure levels (systolic and diastolic blood pressure) of middle age hypertension patients. The result of the present study was supported by the study of Hasnain (2007) who stated that exercise has positive effects on blood pressure levels. Furthermore, adjusted mean systolic blood pressure decreased by 9.0 per cent in the intervention group and 2.33 per cent in the control group, according to their findings. Similarly, the intervention group's adjusted mean diastolic pressure decreased by 7.42 per cent while the control group's stayed basically unaltered.
Exercise has benefits that are comparable to those of pharmacological treatment and should be strongly promoted. Most hypertension people may exercise safely if the programme is well organised, and it also has other key health advantages related to their CVD (cardiovascular disease) risk factors. As a result, it's critical to prescribe exercise to patients who have hypertension or are at risk of developing hypertension, just as you would any other successful medication (Baster-Brooks & Baster, 2005). In hypertension, consistent aerobic activity lowers blood pressure. Regular exercise improved physical performance and lowered blood pressure during effort, as measured by maximal oxygen uptake and lactate curves. The cardiac index and arterial compliance were unaltered. Even in people who don't respond well to medical treatment, physical activity can lower blood pressure. It should be part of the treatment plan for resistant hypertension (Dimeo et al., 2012). In men and women with moderate hypertension, exercise also lowers blood pressure (James et al., 2014).
In persons who have mild to moderate hypertension, aerobic fitness exercise lowers blood pressure by about 7/5 mmHg. Post-exercise hypotension is the result of a single bout of physical exertion resulting in a sharp drop in blood pressure. Physical activity in repeated sessions is thus a technique for lowering blood pressure, although regular exercise is essential to achieve a long-term drop in pressure (Börjesson, Onerup, Lundqvist & Dahlöf, 2016). Physical exercises should also be included in the initial treatment of hypertension patients, with the goal of avoiding or reducing the number and dosage of medications. For inactive and hypertensive individuals, clinically significant blood pressure reductions can be achieved with a relatively small increase in physical activity above the level typically used for inactive individuals; additionally, the exercise volume required to reduce blood pressure can be relatively small, making it possible for even inactive individuals to achieve it (Monteiro & Sobral Filho, 2004).
In males with stage 1 or 2 essential hypertension, aerobic activity resulted in a slight reduction in resting systolic and diastolic blood pressures. Exercise is one example of a lifestyle transformation that may play a role in lowering hypertension risk (Mughal, Alvi, Akhund & Ansari, 2001). In African-American men with severe hypertension, regular exercise reduced blood pressure and left ventricular hypertrophy. After 16 weeks, the mean (SD) diastolic blood pressure had decreased from 88.7 to 83.8 mm Hg in those who exercised, while it had increased slightly from 88.6 to 90.7 mm Hg in those who did not (Peter et al., 2005).
Findings, Conclusion and Recommendations
Findings
Based on data analysis, the researcher found the following findings are drawn;
1. The analyzed data revealed that there is no significant difference in blood pressure levels (Diastolic and Systolic) between the control group and experimental group in the pre-test (p > 0.05) (Table 4.3).
2. It has been found that the nitric oxide dump exercise produced a positive effect on the blood pressure level of the experimental group because the diastolic blood pressure is (sig.= .007 < ?= 0.05) and systolic (sig.= .043 < ?= 0.05) (Table 4.4).
3. When comparing the results of diastolic and systolic blood pressure levels of the control group in pre- and post-test, the analyzed data indicated that the control group remained the same in both tests and no significant change occurred in blood pressure level without any treatment (Sig.= .678, .065 < 0.05) (Table 4.5).
4. When comparing the results of diastolic and systolic blood pressure levels of the experimental group in pre- and post-test, the data revealed that the experimental group was changed in both tests and significant differences occurred in blood pressure level based on given treatment (Sig.= .0.00, .043 > 0.05) (Table 4.6).
Conclusion
The current field experimental research study was conducted to determine the effect of nitric oxide dump exercise on blood pressure levels among middle-aged hypertension patients of district Karak, KP, Pakistan. Results of the study indicated that the mean score of diastolic blood pressure level in the pre-test was 84.20±2.61 and in the post-test was 80.90± 1.28. In the same way, the mean score of systolic blood pressure level in the pre-test was 135.40±2.63 and in the post-test was 118.90±31.95.
Considering the t-Test results, the analyzed statistics revealed statistically significant differences in diastolic and systolic blood pressure levels of the intervention group in pre- and post-test. As a result, these findings tend to indicate that nitric dump oxide exercise can help in reducing the blood pressure levels of hypertension patients. The results obtained through the current study justify the use of nitric dump oxide exercise, as one of the important interventions to reduce blood pressure levels of hypertension patients.
Recommendations
1. Awareness programs regarding the benefits of physical activity/exercise may be conducted in different corners of the country.
2. The community members may get involved in daily physical activity. They must be motivated toward physical activity by ensuring that daily physical activity /exercise is considered a health indicator.
3. The nitric dump exercise used in the current study can be recommended as part of the intervention for hypertension patients.
References
- AbouElmagd, M. (2016). Benefits, need and importance of daily exercise. Int. J. Phys. Educ. Sports Health, 3(5), 22-27.
- Anchala, R., Kannuri, N. K., Pant, H., Khan, H., Franco, O. H., Di Angelantonio, E., & Prabhakaran, D. (2014). Hypertension in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence, awareness, and control of hypertension. Journal of hypertension, 32(6), 1170-1185.
- Baster-Brooks, C., & Baster, T. (2005). Exercise and hypertension. Australian family physician, 34(6), 300-310. 0
- Börjesson, M., Onerup, A., Lundqvist, S., & Dahlöf, B. (2016). Physical activity and exercise lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension: narrative review of 27 RCTs. British journal of sports medicine, 50(6), 356-361.
- Boyer, J. L., & Kasch, F. W. (1970). Exercise therapy in hypertensive men. Jama, 211(10), 1668-1671.
- Carretero, O. A., & Oparil, S. (2000). Essential hypertension: part I: definition and etiology. Circulation, 101(3), 329-335.
- Chobufo, M. D., Gayam, V., Soluny, J., Rahman, E. U., Enoru, S., Foryoung, J. B., & Nfor, T. (2020). Prevalence and control rates of hypertension in the USA: 2017–2018. International Journal of Cardiology Hypertension, 30(9), 950-1080.
- Choudhury, A., & Lip, G. Y. H. (2005). Exercise and hypertension. Journal of human hypertension, 19(8), 585-587.
- Collier, S. R., Kanaley, J. A., Carhart, R., Frechette, V., Tobin, M. M., Hall, A. K., & Fernhall, B. (2008). Effect of 4 weeks of aerobic or resistance exercise training on arterial stiffness, blood flow and blood pressure in pre-and stage-1 hyper-tensive. Journal of human hypertension, 22(10), 678- 686.
- Diaz, K. M., & Shimbo, D. (2013). Physical activity and the prevention of hyper- tension. Current hypertension reports, 15(6), 659-668.
- Dimeo, F., Pagonas, N., Seibert, F., Arndt, R., Zidek, W., & Westhoff, T. H. (2012). Aerobic exercise reduces blood pressure in resistant hypertension. Hypertension, 60(3), 653-658.
- Fryar, C. D., Ostchega, Y., Hales, C. M., Zhang, G., & Kruszon-Moran, D. (2017). Hypertension prevalence and control among adults: United States, 32(11), 1243-1254.
- Gulam, A. (2016). Recreation–need and importance in modern society. International Journal of Physiology, Nutrition and Physical Education, 1(2), 157-160.
- Hasnain, M. (2007). Impact of exercise (walking) on blood pressure levels in African American adults with newly diagnosed hypertension. Ethnicity & disease, 17 (1), 503-512.
- Hirawa, N., Umemura, S., & Ito, S. (2019). Viewpoint on guidelines for the treatment of hypertension in Japan. Circulation Research, 124(7), 981-983.
- Hird, T. R., Zomer, E., Owen, A. J., Magliano, D. J., Liew, D., & Ademi, Z. (2019). Productivity burden of hypertension in Australia: a life table modeling study. Hypertension, 73(4), 777-784.
- Hu, G., Barengo, N. C., Tuomilehto, J., Lakka, T. A., Nissinen, A., & Jousilahti, P. (2004). Relationship of physical activity and body mass index to the risk of hypertension: a prospective study in Finland. Hypertension, 43(1), 25-30. I
- Ibrahim, M. M., & Damasceno, A. (2012). Hypertension in developing countries. The Lancet, 380(9841), 611-619.
- James, P. A., Oparil, S., Carter, B. L., Cushman, W. C., Dennison-Himmelfarb, C., Handler, J., & Ortiz, E. (2014). 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). Jama, 311(5), 507-520.
- Kearney, P. M., Whelton, M., Reynolds, K., Muntner, P., Whelton, P. K., & He, J. (2005). Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The lancet, 365(9455), 217- 223.
- Kurnianto, A., Kurniadi Sunjaya, D., Ruluwedrata Rinawan, F., & Hilmanto, D. (2020). Prevalence of hypertension and its associated factors among Indonesian adolescents. International Journal of Hypertension, 16(4), 2330-2350.
- McLean, R. M., Williams, S., Mann, J. I., Miller, J. C., & Parnell, W. R. (2013). Blood pressure and hypertension in New Zealand: results from the 2008/09 Adult Nutrition Survey. New Zealand Medical Journal, 126(12), 2213-2220.
- Monteiro, M. D. F., & Sobral Filho, D. C. (2004). Physical exercise and blood pressure control. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte, 10(3), 513-516.
- Moreau, K. L., Degarmo, R., Langley, J., McMahon, C. O. L. L. E. E. N., Howley, E. T., Bassett Jr, D. R., & Thompson, D. L. (2001). Increasing daily walking lowers blood pressure in postmenopausal women. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 33(11), 1825-1831.
- Mughal, M. A., Alvi, I. A., Akhund, I. A., & Ansari, A. K. (2001). The effects of aerobic exercise training on resting blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Journal Pakistan Medical Association, 51(6), 222-225.
- Olives, C., Myerson, R., Mokdad, A. H., Murray, C. J., & Lim, S. S. (2013). Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in United States counties, 2001–2009. PloS one, 8(4), 60-308.
- Paffenbarger JR, R. S., Thorne, M. C., & Wing, A. L. (1968). Chronic disease in former college students. VIII. Characteristics in youth predisposing to hyper-tension in later years. American Journal of Epidemiology, 88(1), 25-32.
- Pedrosa, R. P., Drager, L. F., Gonzaga, C. C., Sousa, M. G., de Paula, L. K., Amaro, A. C., & Lorenzi-Filho, G. (2011). Obstructive sleep apnea: the most common secondary cause of hypertension associated with resistant hypertension. Hypertension, 58(5), 811-817.
- Peltzer, K., & Pengpid, S. (2018). The prevalence and social determinants of hypertension among adults in Indonesia: a cross-sectional population-based national survey. International journal of hypertension, 150(18), 1445-1456.
- Penedo, F. J., & Dahn, J. R. (2005). Exercise and well-being: a review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity. Current opinion in psychiatry, 18(2), 189-193.
- Peter, I., Shearman, A. M., Zucker, D. R., Schmid, C. H., Demissie, S., Cupples, L. A., & Levy, D. (2005). Variation in estrogen-related genes and cross-sectional and longitudinal blood pressure in the Framingham Heart Study. Journal of hypertension, 23(12), 2193- 2200.
- Prevention (US). Office of Public Health Preparedness. (2011). Public health preparedness: 2011 state-by-state update on laboratory capabilities and response readiness planning. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Office of Public Health Preparedness and Response
- Wen, H., & Wang, L. (2017). Reducing effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure of essential hypertensive patients: A meta- analysis. Medicine, 96(11).
- Whelton, S. P., Chin, A., Xin, X., & He, J. (2002). Effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Annals of internal medicine, 136(7), 493-503.
- World Health Organization. (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021) (No. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02). World Health Organization.
- Xing, L., Liu, S., Jing, L., Li, S., Tian, Y., Zhang, R., & Pan, G. (2020). Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in Rural Northeast China: 2008 to 2018. BioMed Research International, 141(15), 4450-4460.
- Zafar, F., Tariq, W., Shoaib, R. F., Shah, A., Siddique, M., Zaki, A., & Assad, S. (2018). Frequency of ischemic stroke subtypes based on toast classification at a tertiary care center in Pakistan. Asian journal of neurosurgery, 13(4), 984.
Cite this article
-
APA : Ullah, H., Aslam, M., & Ullah, I. (2022). Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII(III), 30-45. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2022(VII-III).05
-
CHICAGO : Ullah, Hameed, Muhammad Aslam, and Inam Ullah. 2022. "Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII (III): 30-45 doi: 10.31703/gdddr.2022(VII-III).05
-
HARVARD : ULLAH, H., ASLAM, M. & ULLAH, I. 2022. Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak. Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII, 30-45.
-
MHRA : Ullah, Hameed, Muhammad Aslam, and Inam Ullah. 2022. "Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII: 30-45
-
MLA : Ullah, Hameed, Muhammad Aslam, and Inam Ullah. "Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak." Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII.III (2022): 30-45 Print.
-
OXFORD : Ullah, Hameed, Aslam, Muhammad, and Ullah, Inam (2022), "Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak", Global Drug Design & Development Review, VII (III), 30-45
-
TURABIAN : Ullah, Hameed, Muhammad Aslam, and Inam Ullah. "Effects of Nitric Oxide Dump Exercise upon Blood Pressure Levels of Middle-aged Hypertension Patients: A Study of District Karak." Global Drug Design & Development Review VII, no. III (2022): 30-45. https://doi.org/10.31703/gdddr.2022(VII-III).05